Let's talk money, honey. Specifically, government money. We've all heard whispers of the mythical GS pay scale, a complex system that dictates the salaries of federal employees. But what does it actually mean for those of us clocking in outside the hallowed halls of government? Does it affect our paychecks? Our job prospects? Our very existence?
The General Schedule (GS) pay scale isn't just a bureaucratic quirk; it's a massive system impacting millions of workers and shaping the economic landscape. Understanding its intricacies can provide insight into everything from wage stagnation to the cost of living in certain areas. This isn't just about Uncle Sam's employees; it's about the rest of us, too.
So, buckle up as we navigate the labyrinthine world of the federal pay system. We'll dissect the GS pay grades, explore its impact on the private sector, and answer the burning question: how does the GS pay scale affect *you*?
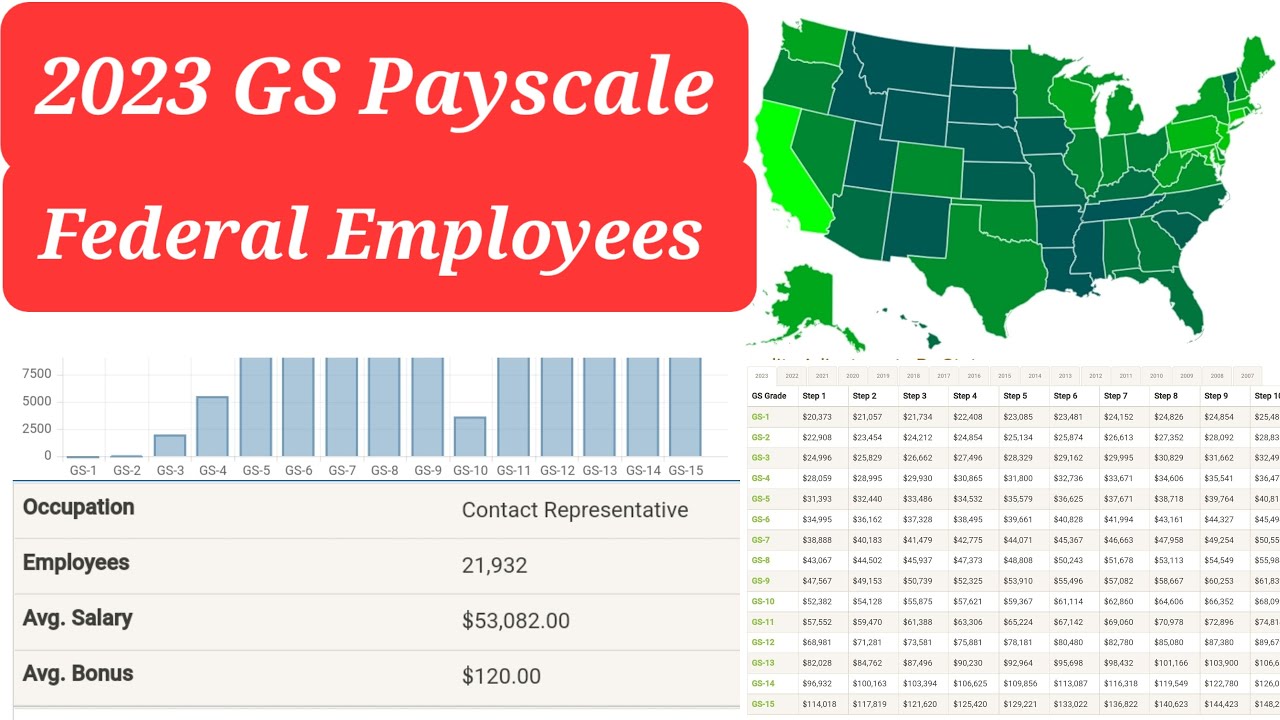
Think of the GS pay system as a meticulously crafted ladder, each rung representing a different grade and salary level. From entry-level positions to seasoned professionals, each federal job is assigned a GS level based on factors like required education, experience, and job responsibilities. This standardized approach aims to ensure fair and equitable compensation within the government.
But the GS pay scale doesn't exist in a vacuum. Its influence extends beyond federal agencies, subtly impacting the private sector and the overall job market. Understanding its ripple effects is crucial for anyone navigating the modern workplace.
The GS pay scale has its roots in the Classification Act of 1923, aiming to standardize federal positions and compensation. Over time, it has evolved, reflecting economic shifts and societal changes. Its importance lies in ensuring fair pay for government employees and maintaining a competitive edge in attracting talent. However, issues like locality pay adjustments and perceived pay gaps between government and private sector jobs continue to be debated.
The GS pay scale is divided into 15 grades (GS-1 through GS-15), each with 10 steps within each grade. A GS-5, Step 1 employee, for example, would earn less than a GS-5, Step 10 employee. Locality pay adjustments further modify base salaries based on the cost of living in different geographic areas.
While a direct correlation is complex, the GS pay scale can indirectly influence private sector wages, particularly in areas with a high concentration of federal employees. It can also serve as a benchmark for salary negotiations in certain industries.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the GS Pay Scale
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Transparency and Structure | Rigidity and Limited Negotiation |
| Job Security and Benefits | Potential Pay Gaps with Private Sector |
| Clear Career Progression | Bureaucracy and Slow Advancement |
Navigating the complexities of the GS pay scale can be daunting. But with a little research and understanding, you can gain valuable insight into how this system impacts the larger job market and your own career prospects.
Frequently Asked Questions about the GS Pay Scale:
1. How is locality pay calculated? (Answer: Based on cost of living data for different geographic areas.)
2. What are within-grade increases? (Answer: Salary increases within a specific GS grade based on performance and time in grade.)
3. How can I find the current GS pay tables? (Answer: The U.S. Office of Personnel Management website.)
4. Does the GS pay scale apply to all federal employees? (Answer: Not all, some agencies have separate pay systems.)
5. How does the GS pay scale compare to private sector salaries? (Answer: Varies greatly depending on the industry, location, and specific job.)
6. Can I negotiate my salary on the GS pay scale? (Answer: Limited negotiation is possible, primarily at the time of hiring.)
7. What are some common misconceptions about the GS pay scale? (Answer: That it's always lower than private sector pay, that it's easy to advance quickly.)
8. How does the GS pay scale influence the overall economy? (Answer: Impacts government spending, influences local economies, and indirectly affects private sector wages.)
One trick to understanding the GS pay system is to focus on locality pay. Recognizing how location impacts salary can be crucial when comparing federal and private sector job offers.
In conclusion, the General Schedule (GS) pay scale, though designed for federal employees, has a ripple effect across the broader job market. Understanding its complexities, from its historical origins to its current impact on private sector wages, allows for a more informed perspective on salary negotiations, career choices, and the economic landscape as a whole. By demystifying this seemingly arcane system, we can all better navigate the complexities of the modern workplace and make informed decisions about our own career paths. While the GS pay scale itself may not directly dictate your salary if you're not a federal employee, its influence on the broader economy and the job market is undeniable. Knowing how it works empowers you to understand market trends, compare compensation packages, and make strategic decisions about your future. So, the next time you hear about the GS pay scale, remember, it's not just about government workers; it's about all of us.
Unlocking design potential with sherwin williams green hues
Unlock serenity with benjamin moores dune gray
Navigating conflict resolution tennessee rule 31 mediator training